Introduction
Gingivitis is a common but often overlooked oral health condition that affects a large percentage of the population. It is the earliest stage of gum disease and, if left untreated, can progress to more severe conditions like periodontitis. Understanding gingivitis symptoms, gingivitis treatment, and the overall implications of gum disease is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing long-term complications. This article explores the causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures for gingivitis.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by bacterial plaque buildup along the gumline. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gum tissue, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding. Unlike advanced gum disease, gingivitis does not involve irreversible bone or tissue damage, making it a treatable condition if addressed early.
Gingivitis Symptoms
Recognizing gingivitis symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Common signs include:
- Red and Swollen Gums – Healthy gums should be firm and pink, but gingivitis causes them to become inflamed and tender.
- Bleeding Gums – One of the most noticeable gingivitis symptoms is bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis) – Persistent bad breath can be a sign of gum disease due to bacterial buildup.
- Gum Recession – In some cases, gums may begin to pull away from the teeth.
- Tenderness and Discomfort – The gums may feel sore or sensitive when eating or brushing.
Causes of Gingivitis
Several factors contribute to the development of gingivitis, including:
- Poor Oral Hygiene – Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use – Tobacco weakens the immune system, making it harder for gums to heal.
- Hormonal Changes – Pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can increase gum sensitivity.
- Certain Medications – Some drugs reduce saliva flow, leading to plaque buildup.
- Nutritional Deficiencies – Lack of vitamins, particularly vitamin C, can contribute to gum disease.
- Medical Conditions – Diseases like diabetes and immune disorders can make individuals more susceptible to gingivitis.
Gingivitis Treatment
The good news is that gingivitis treatment is highly effective when started early. Some of the most recommended gingivitis treatment options include:
- Professional Dental Cleaning – Removing plaque and tartar buildup through scaling and polishing.
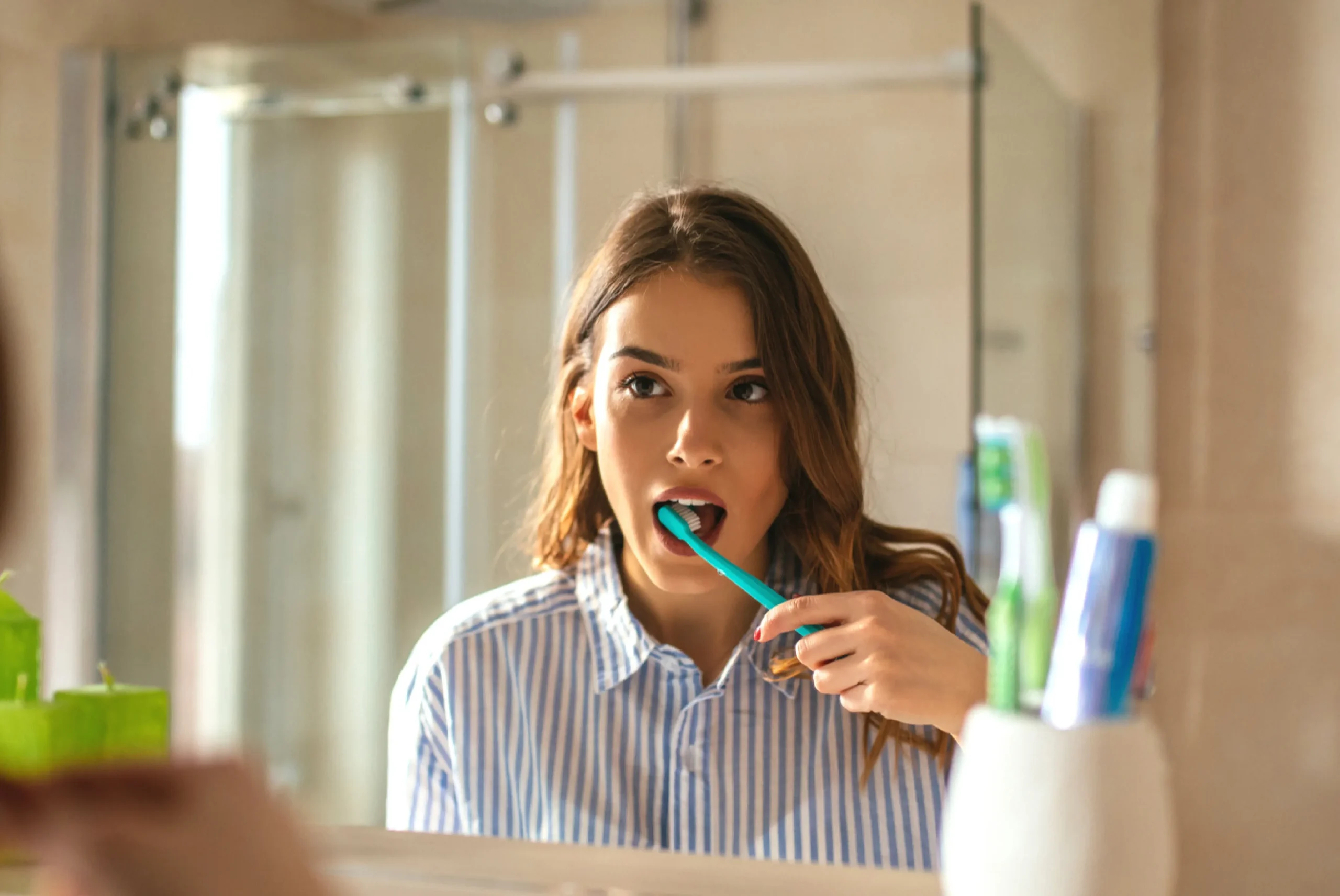
- Improved Oral Hygiene – Brushing twice a day and flossing regularly can prevent plaque accumulation.
- Antibacterial Mouthwash – Helps reduce bacterial growth and inflammation.
- Medicated Toothpaste – Special formulations designed for gum disease can aid in healing.
- Healthy Diet – Consuming foods rich in vitamins and antioxidants supports gum health.
- Regular Dental Visits – Routine check-ups help detect and treat gingivitis before it worsens.
- Avoiding Tobacco – Quitting smoking can significantly improve gum health.
- Hydration – Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria.
- Stress Management – Reducing stress levels can improve immune response and gum resilience.
- Using a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush – This prevents further irritation to sensitive gums.

Gum Disease and Its Progression
If left untreated, gingivitis can advance into more severe stages of gum disease, known as periodontitis. Unlike gingivitis, periodontitis involves the destruction of gum tissue and bone that support the teeth. This can lead to tooth mobility, loss, and other serious oral health complications. Regularly addressing gingivitis symptoms and seeking appropriate gingivitis treatment can help prevent this progression.
Preventing Gingivitis
Prevention is the best approach to managing gingivitis and reducing the risk of gum disease. Some essential preventive measures include:
- Maintaining Proper Oral Hygiene – Brushing and flossing daily help remove plaque before it hardens into tartar.
- Regular Dental Cleanings – Professional cleanings help keep the gums healthy.
- Balanced Diet – Eating nutrient-rich foods supports overall oral health.
- Avoiding Sugary Foods and Drinks – Sugar contributes to plaque formation and bacterial growth.
- Managing Health Conditions – Controlling conditions like diabetes can reduce susceptibility to gingivitis.
- Using Antiseptic Mouthwash – Helps kill bacteria and prevent plaque buildup.
- Staying Hydrated – Keeps the mouth clean and reduces bacterial accumulation.
- Quitting Smoking – Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease.
- Regular Gum Massages – Stimulates blood flow and promotes gum health.
- Replacing Your Toothbrush Regularly – A worn-out toothbrush is less effective in plaque removal.
Advanced Considerations for Gingivitis Management
Gingivitis is not just an isolated oral health issue; it has been linked to several systemic diseases. Recent research has shown a correlation between gum disease and conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and even Alzheimer’s. Chronic inflammation in the gums may contribute to inflammation throughout the body, increasing the risk of other serious health issues.
Another crucial factor in gingivitis treatment is recognizing genetic predispositions. Some individuals may be more prone to gum disease due to their genetic makeup. Identifying risk factors early can help in adopting preventive measures before symptoms become severe.
Additionally, modern advancements in dentistry offer new solutions for gingivitis treatment. Laser therapy is emerging as a promising non-invasive treatment for gum disease, reducing inflammation and promoting tissue healing. Other cutting-edge treatments include probiotics specifically designed for oral health, which help balance the bacterial ecosystem in the mouth and reduce inflammation.
Furthermore, lifestyle changes play a significant role in gingivitis management. A well-balanced diet rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals strengthens gum tissue and supports the immune system. Reducing stress through activities like yoga and meditation can also positively impact oral health by lowering inflammation and boosting immune function.
Ultimately, treating gingivitis requires a multi-faceted approach that includes proper oral hygiene, professional care, and overall lifestyle improvements. By staying proactive, individuals can maintain healthy gums and prevent the complications associated with gum disease.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a common and treatable condition, but if left unchecked, it can lead to more serious gum diseases that affect not only oral health but overall well-being. Early recognition of symptoms and prompt treatment, such as professional cleanings and improved oral hygiene, are essential in managing and reversing gingivitis. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, avoiding smoking, and managing medical conditions like diabetes also play key roles in preventing gum disease. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can protect their gums and reduce the risk of more severe complications like periodontitis. Remember, regular dental check-ups and consistent oral care are crucial for keeping your gums healthy, and with the right approach, gingivitis can be easily managed to ensure long-term oral health.