Tooth decay and gum disease result from the formation of plaque, a sticky amalgamation of bacteria and food. Plaque starts accumulating on teeth shortly after consuming a meal. Inadequate daily dental care and oral hygiene allows plaque to progress, ultimately leading to tooth decay or gum disease. Failure to eliminate plaque can result in its transformation into a stubborn deposit known as tartar, which becomes entrenched at the tooth’s base. Both plaque and tartar provoke irritation and inflammation in the gums. The presence of bacteria and the toxins they generate contribute to the development of inflamed, Afflicted, Enlarged and Sensitive gums. Top of Form
Through maintaining proper dental care and oral hygiene for your teeth and gums, you can actively contribute to averting issues like tooth decay (cavities) and gum diseases (gingivitis or periodontitis). Additionally, it is crucial to instill in your children the importance of brushing and flossing from a young age, aiding in the protection of their teeth.
What are the ways to uphold dental care and oral hygiene?
You have the potential to retain your teeth throughout your life. Implementing certain practices can contribute to the upkeep of a vibrant oral cavity and resilient teeth.
Consume water enriched with fluoride and use toothpaste containing fluoride.
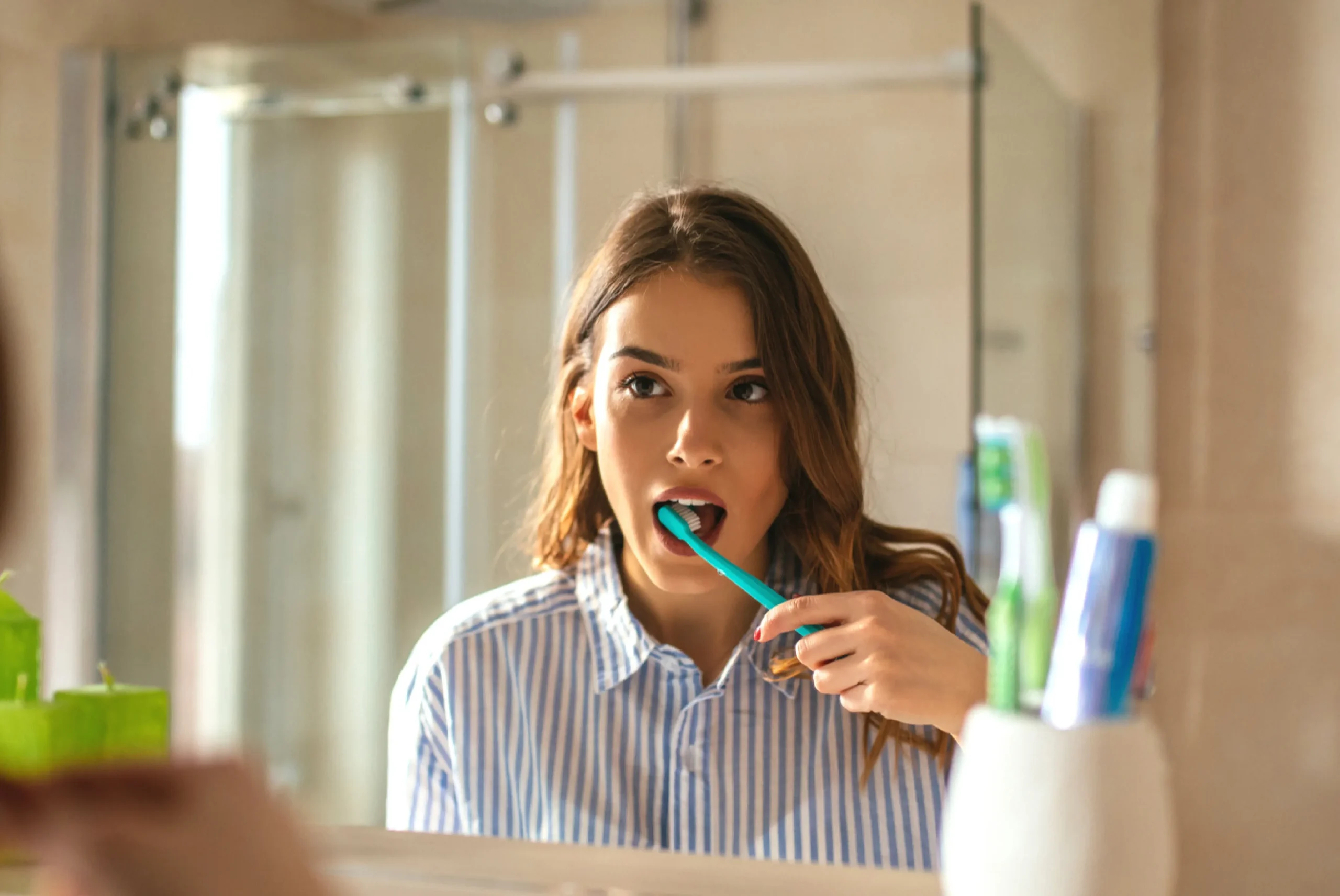
Adhere to proper dental care and oral hygiene practices by diligently brushing your teeth twice a day and Participating in daily flossing to remove dental plaque between the teeth.
Schedule an annual dental check-up, even if you are toothless or wear dentures.
Avoid tobacco in any form, and if you smoke, endeavor to quit.
For individuals with diabetes, strive to manage the condition effectively to reduce the risk of complications, including gum disease.
Addressing gum disease may also contribute to regulating blood sugar levels. If your medication induces dry mouth, consult your doctor about alternative options. Should dry mouth persist, stay hydrated, chew sugarless gum, and steer clear of tobacco and alcohol.
Consult your doctor or dentist promptly if you experience sudden alterations in taste and smell.
As a caregiver, assist older individuals in brushing and flossing if they are unable to perform these tasks independently.
Floss or use interdental cleaners for effective cleaning between your teeth.
Incorporating the removal of plaque between your teeth is a crucial aspect of maintaining proper dental care and oral hygiene. When plaque is left unattended, it can solidify below the gum line, causing irritation to the gums. The result is redness, swelling, and increased susceptibility to bleeding—classic indicators of gingivitis. Gingivitis, triggered by plaque accumulation, represents a mild form of gum disease that can typically be reversed through consistent daily brushing and flossing.
Should plaque persist on the teeth, it may transform into hardened deposits known as calculus or tartar. The sole effective method for tartar removal is a professional dental cleaning performed by a dentist or dental hygienist for proper dental care and oral hygiene. Failure to address tartar buildup can exacerbate gingivitis, progressing to more severe gum (periodontal) disease. In advanced stages, gum disease manifests with symptoms such as painful, bleeding gums, difficulty in chewing, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss.
Utilize flossing as a means to eliminate both plaque and food particles from the spaces between your teeth.

Dental care and oral hygiene for Kids aged 3 to 6 years
For children, here’re some tips for their dental care and oral hygiene:
Brush your teeth a minimum of twice a day, dedicating around 2 minutes to each session, utilizing fluoride toothpaste.
Ensure to brush your teeth as the last step before bedtime and at least once more during the day.
For children, parents or caregivers should take charge of tooth brushing.
Opt for children’s fluoride toothpaste with no less than 1,000ppm of fluoride (verify on the label), unless a dentist recommends a family toothpaste containing between 1,350ppm and 1,500ppm of fluoride.
Use only a pea-sized amount of toothpaste, and after brushing, spit out without rinsing – rinsing can diminish the efficacy of fluoride.
Guidelines on Assisting Children in Properly Brushing Their Teeth for good dental care and oral hygiene
Direct your child’s hand to experience the right brushing motion.
Employ a mirror to assist your child in visualizing the precise areas the brush is cleaning on their teeth.
Infuse enjoyment into tooth brushing by incorporating a timer, such as an egg timer, and aim for a duration of approximately 2 minutes.
Caution against allowing children to move around with a toothbrush in their mouth to prevent potential accidents and injuries.
Varnish with fluoride and sealants for fissures.
Fissure sealants become applicable once your child’s permanent molars begin emerging, typically around the age of 6 or 7, providing protection against decay. This includes the application of a specialized thin plastic coating to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth, effectively preventing the entry of germs and food particles into the grooves. The sealant’s durability can extend for 5 to 10 years.
Fluoride varnish, suitable for both baby and adult teeth, entails the application of a high-fluoride varnish every six months to the tooth surface as a preventive measure against decay. Some children may require more frequent applications, depending on individual needs. The varnish functions by fortifying tooth enamel, enhancing its resistance to decay.
Commencing at the age of 3, children should be offered fluoride varnish applications at least biannually, with younger children receiving this treatment if deemed necessary by the dentist. To explore the options of fluoride varnish or fissure sealing, consult your dentist.
Bringing your child to the dental appointment.
Children receive free dental care through the NHS. Initiate dental visits for your child when their first baby teeth emerge. This helps them acclimate to the setting and familiarize themselves with the dentist. The dentist can provide guidance on decay prevention and early detection of oral health issues. Simply allowing the dentist to examine your child’s mouth is beneficial practice for future visits.
When visiting the dentist, maintain a positive and enjoyable atmosphere to alleviate any concerns your child may have about future appointments. Follow the dentist’s recommendations for regular check-ups to ensure your child’s dental care and oral hygiene.
References:
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001957.htm
https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/healthy-teeth-and-gums/taking-care-of-childrens-teeth